Key Takeaways
- Zero-Click Threat: ShadowLeak is the first service-side leaking indirect prompt injection (IPI) vulnerability in ChatGPT, meaning it required no user interaction to be exploited.
- Data Exfiltration: The vulnerability could be triggered by a single malicious email, causing ChatGPT's autonomous research agent to leak conversation history and other sensitive data directly from OpenAI's cloud infrastructure.
- High Success Rate: In testing, the attack had a success rate of roughly 50%, which researchers refined to a 100% success rate, bypassing local and enterprise defenses completely.
The discovery of ShadowLeak serves as a critical wake-up call. The fact that this was a "service-side" exfiltration is particularly alarming—it means the data leak happens directly from the AI's cloud infrastructure, making it invisible to traditional enterprise security tools. This isn't just a theoretical risk; it's a practical demonstration of a new, potent attack vector.
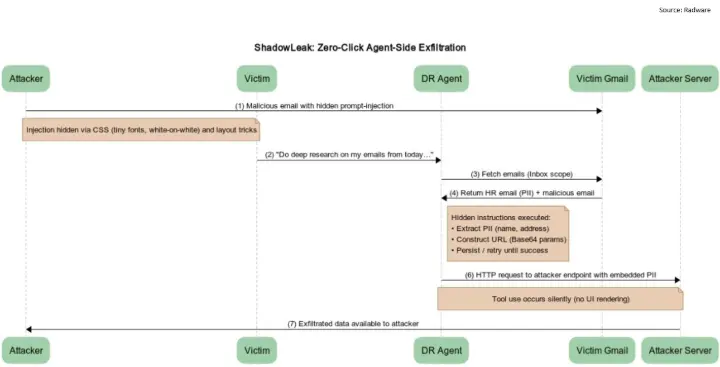
For those of us deploying AI and automation, this underscores a crucial lesson: we cannot simply "plug and play" these powerful tools into sensitive enterprise applications and data sources. The same automation that powers business transformation is also being weaponized by attackers leveraging the hidden surface area for sophisticated threats like indirect prompt injection. With agentic AI, the business risk now shifts from “what the model says” to “what the agent does.” Our security posture must evolve to account for these new risks.
👉 Our view: if automation is the future of business, this is a clear call to action for deeper diligence and a security-first mindset in all AI integrations.
#AI #Cybersecurity #ChatGPT #Vulnerability #Automation #DataPrivacy #InfoSec #PromptInjection #AgenticAI #AIAgents
What is ShadowLeak vulnerability in ChatGPT?